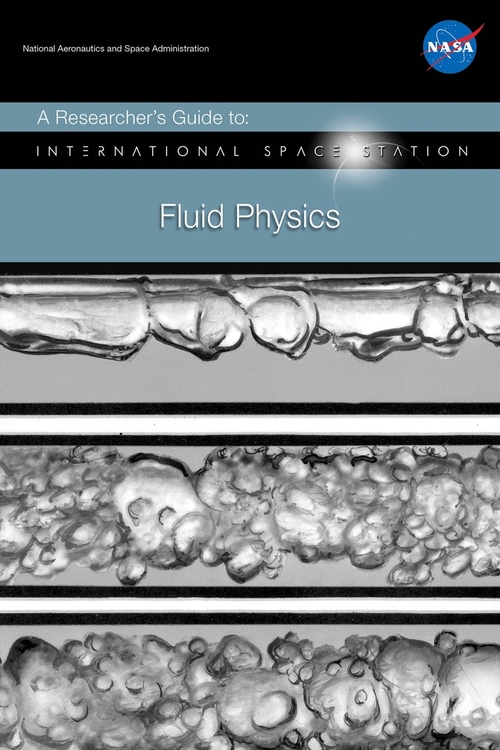
Flying 250 miles above the Earth, the ISS provides a platform for research to improve life on Earth, enable space exploration, and understand the universe. This researcher’s guide is intended to help potential ISS fluid physics researchers plan experiments utilizing the microgravity environment in order to understand how heat and mass transfer affects fluid flows and behavior. It covers the nature of the acceleration environment on ISS, available facilities for conducting fluid physics research, examples of previous microgravity research, and current fluid physics projects being developed for execution on the ISS.
 05.03.2026
05.03.2026
Пуск японской частной ракеты закончился аварией
🔥 Неудачей завершился пуск японской частной РН Kairos-3 с пятью спутниками. 🚀 Ракета стартовала в 02:10 UTC (05:10 мск) с...
Далее 04.03.2026
04.03.2026
Запущена группа спутников Starlink-10.40
4 марта 2026 г. в 10:52 UTC (13:52 мск) с площадки SLC-40 Станции КС США “Мыс Канаверал” (шт. Флорида, США) стартовыми командами...
Далее 02.03.2026
02.03.2026
На орбите группа спутников Starlink-10.41
🚀🇺🇸 2 марта 2026 г. в 02:56 UTC (05:56 мск) с площадки SLC-40 Станции КС США “Мыс Канаверал” (шт. Флорида, США) стартовыми...
Далее 01.03.2026
01.03.2026
Запущена группа спутников Starlink-17.23
🚀🇺🇸 1 марта 2026 г. в 10:10 UTC (13:10 мск) с площадки SLC-4Е Базы КС США “Ванденберг” (шт. Калифорния, США) стартовыми...
Далее